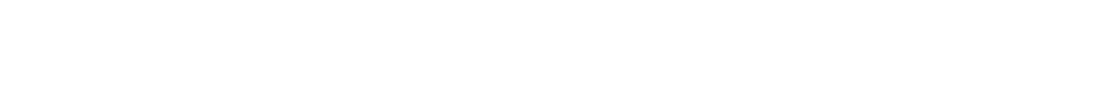Screaming Monsters and Sordid Gays: Ian Bogost’s Alien Phenomenology
I was really looking forward to reading Ian Bogost’s philosophy book, Alien Phenomenology, or What It’s Like to Be a Thing. Two girls who I absolutely admire — one who writes criticism about Thoreau, one who writes plays about Louis Braille — placed praise upon the book, and I was prepared to do similarly.
Ian’s book is bound to object-oriented ontology, a philosophy that posits that “nothing has special status, but that everything exists equally — plumbers, cotton, bonobos, DVDs.” For Ian, the world is composed of units, where “something is always something else.” Humans, the stars of so many philosophies, can neither be separated nor elevated above other things because those things are a part of them and they are a part of those things. While Kant (a bland German boy), Heidegger (a curious Nazi boy), and others put people on a peerless pedestal, Ian puts them in messy dot where millions of encounters occur at once. As Ian explains:
On August 10, 1973, at a boathouse in Southwest Houston, the shovel of a police forensics investigator struck the femur of one of the seventeen corpses excavated that week, victims of serial killer Dean Corll.
The boathouse, the shovel, the police boy, the serial killer — each is a unit, and each unit leads to other units. The serial killer boy probably possessed a mommy and daddy, and his mommy and daddy are units who are entwined with more units. Object-oriented ontology suggests the unceasing character of the Nazis, who were invariably inserting themselves into more land, lives, and histories. Units are all over, and, during World War Two, so were the Nazis.
But not all of object-oriented ontology can be compared to screaming monsters who slaughtered six million you-know-whos and five million ummms. Some of Ian’s philosophy aligns with utterly unpleasant people, like Walt Whitman and Allen Ginsberg. Each of these canonized homosexuals has a penchant for lists. Whitman enumerates his electrified body parts while Ginsberg tells of the objects that have transfixed his tushy. For Ian, “Lists remind us that no matter how fluidly a system may operate, its members nevertheless remain utterly isolated, mutual aliens.” Whitman-Ginsberg types show this shared separateness in a most sordid way. Queer theorist Tim Dean details how homosexuals disclose the inevitable objectification of s-e-x. Disputing Andrea Dworkin’s belief that porn “dehumanizes those whom it fetishizes,” Dean says that all s-e-x, not just the porn kind, “fragments and particularizes.” Such fragmentation is disgustingly displayed in the gay community, whose members, according to Dean, BJ boys through holes in the wall, then spit the c-u-m into a container, which is then funneled into other boys’ tushies.
[Those in Pacific Standard Time, click on image if you want to fucking rock out with me, and turn it up you fags.]
The Nazis & Our Critical Consciousness

I just got done reading Piotr Uklanski’s monograph, The Nazis. Reading here, of course, simply refers to the act of looking, as there are no words in the book (until an index at the end). Uklanski is an artist, a Polish photographer. Although, similar to my own approach to photography, Uklanski doesn’t take photos per se. Rather, he’s sort of a curator, a collector, highlighting, as the New York Times says, “Conceptual attitudes” (the superfluous capital letter on conceptual is NYT, btw).
The Nazis is a book that bears 247 pages of appropriated images of Hollywood, and prevalent European, actors decked out in Nazi regalia. What I’m interested in probing here are the following things: 1) why are there enough stills for this collection to be possible? and 2) why was I interested enough in this book to go through the process of requesting it from WorldCat?
checking back in with Joshua Cohen and Kafka’s Office Writings


I’m sure you’ve all been keeping up this week with Nextbook.org’s five part series on Kafka’s Office Writings, which I first blogged about on Monday. But in case you haven’t, this is a good time to look over what you’ve missed so you can be all caught up for the big (?) finale tomorrow. The series, as I’ve mentioned now several times, is authored by Joshua Cohen, quite possibly the youngest working critic to be described non-ironically as “venerable,” assuming he has ever actually been called that before, which, if he hasn’t–well he has now.
(clicking anywhere on the text of a given day takes you to that day on Nextbook)
+
+
+
+
After you’ve had your fill of nonfiction, consider perhaps some of his other literature. Cohen is the author of five fine books out from presses that Giant readers and contributors alike have deep affection for: A Heaven of Others (Starcherone, 2008), Two Tribal Stories (Small Anchor, 2007), Aleph-Bet: An Alphabet for the Perplexed (Six Gallery, 2007), Cadenza for the Schneiderman Violin Concerto (Fugue State, 2007), The Quorum (Twisted Spoon, 2005). A new novel, Graven Imaginings, is forthcoming from Dalkey Archive. Better get on over to his website and see what the score is.